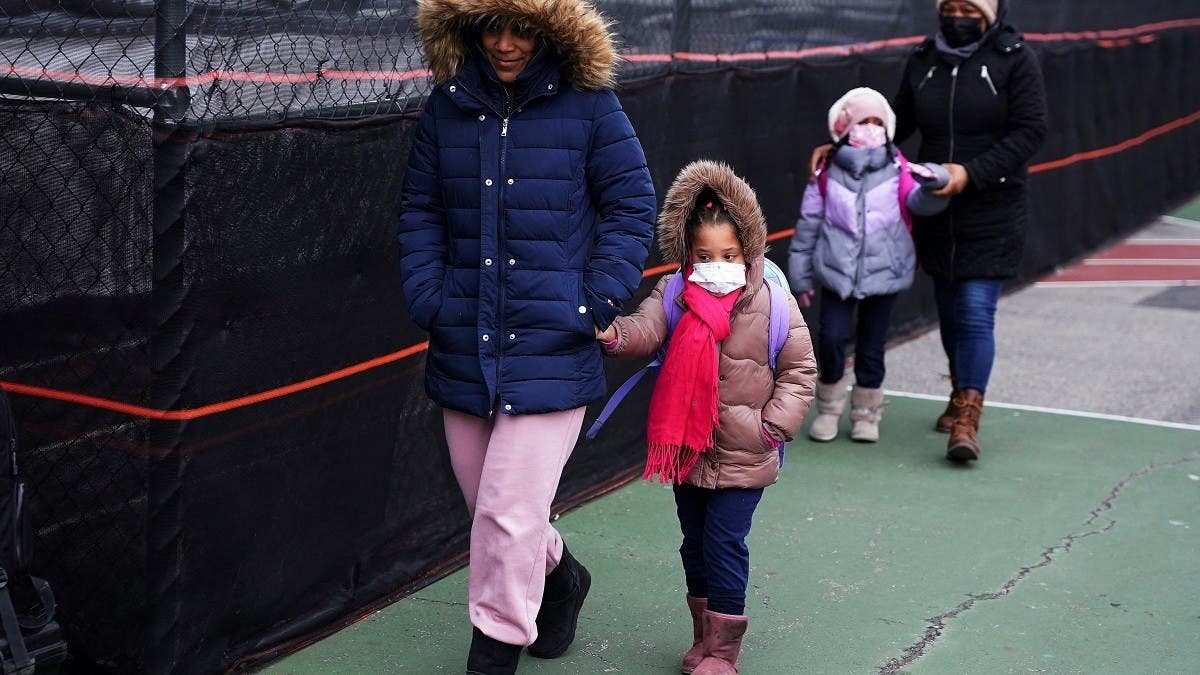
Hospitalizations of US children under 5 with COVID-19 soared in recent weeks to their highest level since the pandemic began, according to government data released Friday on the only age group not yet eligible for the vaccine.
The worrisome trend in children too young to be vaccinated underscores the need for older kids and adults to get their shots to protect those around them, said Dr. Rochelle Walensky, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Read the latest updates in our dedicated coronavirus section.
Since mid-December, as the highly contagious omicron variant has spread furiously around the country, the hospitalization rate in these youngest children has surged to more than 4 in 100,000 youngsters, up from 2.5 per 100,000.
That compares with a current rate of about 1 per 100,000 for children ages 5 to 17, according to CDC data.
In a statement, Walensky said that while children still have the lowest rate of hospitalization of any age group, “pediatric hospitalizations are at their highest rate compared to any prior point in the pandemic.”
At a briefing, she said the numbers include children hospitalized because of COVID-19 and those admitted for other reasons but found to be infected.
She noted that just over 50 percent of children ages 12 to 18 are fully vaccinated and only 16 percent of those 5 to 11 are fully vaccinated.
As of Tuesday, the average number of children and teens admitted to the hospital per day with COVID-19 was 766, double the figure reported just two weeks ago.
At a White House briefing this week, Dr. Anthony Fauci, the top US infectious-disease expert, said many children hospitalized with COVID-19 have other health conditions that make them more susceptible to complications from the virus. That includes obesity, diabetes and lung disease.
Fauci and Walensky have emphasized that one of the best ways to protect the youngest children is to vaccinate everyone else.
Data suggest booster shots offer the best protection against omicron, and CDC this week recommended them for kids as young as 12. Among older ages already eligible, just 34 percent have received them.
The surge in hospitalizations only heightens the concerns of parents worried about how to keep their infants and toddlers safe.
Emily Hojara and Eli Zilke of Sawyer, Michigan, are being extra protective of their daughter Flora, who turns 2 in May. They limit her contact with other children, and no visitors are allowed in the house unless masked, not even grandparents.
“It’s been a struggle, and now with this new variant, I feel it’s knocked us back,’’ Hojara said. She said the new hospitalization data “just reminds you that that anxiety is hovering really close.’’
“It’s scary that she can’t be vaccinated,’’ Hojara said of her daughter.
Dr. Jennifer Kusma, a pediatrician with Chicago’s Lurie Children’s Hospital, said she has seen increasing numbers of kids hospitalized with omicron, and while most aren’t severely ill, she understands parents’ worries.
“As a pediatrician, I really wish we already had that vaccine for these young kids,’’ Kusma said. But she added that what may seem like a long wait should reassure parents that vaccine testing is not being rushed.
Many had hoped the new year might bring a vaccine for young children, but Pfizer announced last month that two doses didn’t offer as much protection as hoped for in youngsters ages 2 to 4.
Pfizer’s study has been updated to give everyone under 5 a third dose, and data is expected in early spring.
Read more: Overwhelmed by omicron surge, US hospitals delay elective surgeries

 World2 years ago
World2 years ago
 World2 years ago
World2 years ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago
 World7 years ago
World7 years ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago