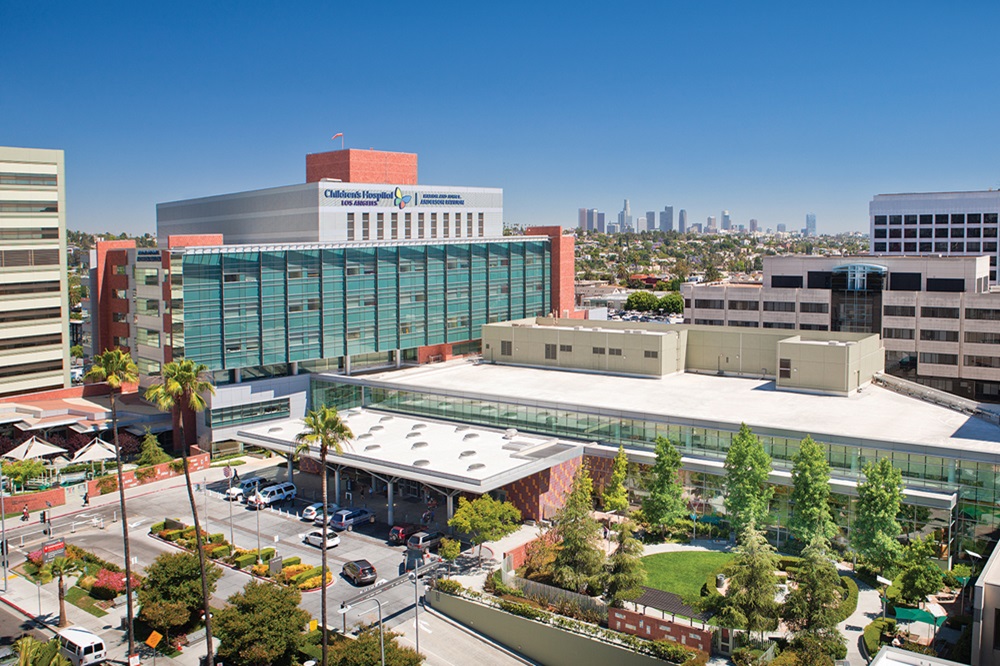
As a leader in pediatric academic medicine, Children’s Hospital Los Angeles (CHLA) has continued to fulfill its mission by making discoveries and advances to enhance health and save lives. Today, Children’s
Hospital Los Angeles was recognized among the top 10 pediatric hospitals in the United
States, according to U.S. News & World Report, which has announced the 2024-25
edition of its annual Best Children’s Hospitals rankings.
The privilege of earning a place on U.S. News Honor Roll of Best Children’s
Hospitals has been conferred upon CHLA 16 years and counting, since the magazine
created the list. Additionally, CHLA retained its No. 1 children’s hospital ranking in U.S.
News’ separate regional survey of Pacific Rim pediatric hospitals, tying with two others
in the region. Children’s Hospital Los Angeles also tied for No. 1 in California and is the
No. 1 pediatric provider in Los Angeles. For the 2024-25 survey, U.S. News did not
publish ordinal rankings for the 10 hospitals that made the Honor Roll. All 10 are
considered equally top tier.
“Being recognized as one of the top children’s hospitals in the country demonstrates our
unwavering commitment and excellence in pediatric healthcare,” says CHLA President
and Chief Executive Officer Paul S. Viviano. “We are committed to enhancing health,
saving lives and providing the best care for children, teens, young adults and the
families we serve. Our dedicated team of doctors, nurses, and staff, all contribute to
helping us put our patients first and are the reason this achievement continues to be
possible.”
U.S. News & World Report also ranked hospitals in 11 individual subspecialties, and
CHLA was ranked in all of these. CHLA earned top-10 recognition in five of the
specialties: Cancer (6), Endocrinology (6), Gastroenterology & GI
Surgery (6), Orthopedics (4) and Urology (4). In all, CHLA earned national recognition
in all 11 specialty areas, including: Cardiology (12), Nephrology
(16), Neurology & Neurosurgery (15), Neonatology (21) and Pulmonology (11).
Children’s Hospital Los Angeles was also honored in U.S. News & World Report’s
newest category—Pediatric and Adolescent Behavioral Health—which was added in
response to the national mental health crisis affecting children, adolescents and young
adults. For this first year, the publication identified CHLA among a group of 50 pediatric
hospitals providing the highest quality, compassionate care for youth coping with
behavioral and emotional challenges. CHLA’s Behavioral Health Institute provides
seamless care of Psychiatry, Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrics, Psychology, and
Social Work services, including for specific conditions such as autism spectrum disorder
and other developmental disabilities.
“Being ranked as one of the nation’s top hospitals in the country reflects our ability to
offer and provide specialized pediatric services, including world class care for complex
cases – rare and chronic conditions treated by multi-disciplinarian teams of pediatric
clinicians. This ability to care for these unique children is what sets CHLA apart from
other hospitals,” says CHLA Chief Medical Officer James Stein, MD, MSc. “At CHLA
we deliver more pediatric care for patients with complex conditions than any other
hospital in California. We are constantly advancing our practices and research to
provide solutions that continue to save lives.”
Children’s Hospital Los Angeles has more than 8,000 team members—including nearly
1,000 pediatric specialist physicians. The hospital performs nearly 16,000 surgeries and
conducts more than 723,000 patient visits each year. As a pediatric academic medical
center, CHLA delivers world-class medical care; conducts groundbreaking scientific
research to develop new treatments and new cures for childhood diseases at The
Saban Research Institute of CHLA; and operates one of the largest pediatric training
programs in the country for physicians, nurses and other specialists.
CHLA is one of the nation’s premier pediatric institutions with services and outcomes for
rare and complex conditions among the best in the world. It has treated patients from
more than 90 countries and has a dedicated Center for Global Health to support the
unique needs of international patients and families traveling to CHLA for specialty and
complex care needs. International patients and families can contact the Center for
Global Health at internationalpatientreferrals@chla.usc.edu.
“Our Center for Global Health supports the unique needs of international patients with a
single point-of-contact to make it easy for them and their families to access and
navigate all aspects of care,” said Yadira Torres, Executive Director of the Global Health
Program at CHLA. “We also make it a priority to be culturally diverse, offering services
in over 34 languages, so families can easily and effectively communicate with our
doctors, nurses and medical staff.”
Each year, U.S. News & World Report and research firm RTI International develop the
Best Children’s Hospital list. For 2024-25, The Best Hospitals specialty rankings
assessed nearly 200 pediatric hospitals—including freestanding institutions like CHLA,
children’s hospitals that are part of a larger health system, and specialty pediatric
centers. Each was scored across hundreds of benchmarks, including quality and safety
performance; patient outcomes; peer recognition; research; technology; commitment to
care that is diverse, equitable and inclusive; certifications; third-party awards; and other
data points provided by each hospital.

 World3 years ago
World3 years ago
 World3 years ago
World3 years ago
 Business1 year ago
Business1 year ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago
 World7 years ago
World7 years ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago





