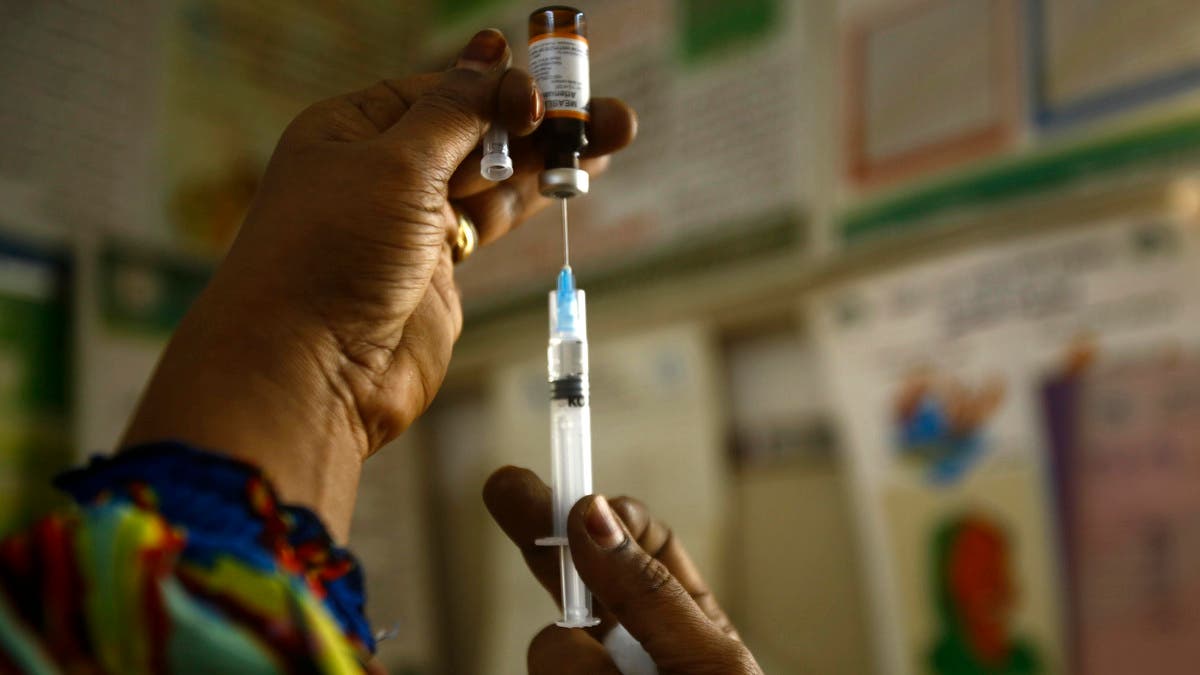
Africa is seeing a surge of outbreaks of preventable diseases as a result of disruptions caused by the coronavirus pandemic, the World Health Organization said on Thursday.
The continent recorded a 400 percent increase in measles, to more than 17,000 cases between January and March, compared to the same period last year, Dr. Benido Impouma, a WHO expert in Africa, told a press briefing.
Two years of disruptions by the coronavirus pandemic have had “major effects on the provision of routine health services, with immunization being seriously affected” in many countries, he said.
For the latest headlines, follow our Google News channel online or via the app.
Twenty-four countries confirmed outbreaks of polio last year, four times more than in 2020. Last year, 13 countries reported new outbreaks of yellow fever, rising from nine in 2020 and three in 2019, according to WHO figures.
“The rise in outbreaks of other vaccine-preventable diseases is a warning sign,” Dr. Matshidiso Moeti, the WHO regional director for Africa, said in a statement. “As Africa works hard to defeat COVID-19, we must not forget other health threats. Health systems could be severely strained not only by COVID-19 but by other diseases.”
The continent of 1.3 billion people has reported 11.4 million COVID-19 cases, including 252,000 deaths, according to figures from the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although the virus had been trending downward since January, the WHO reported a rise in cases Thursday driven by a doubling of infection rates in South Africa, the African country most affected by the pandemic.
Impouma, the WHO official, said that in the wake of the pandemic the agency seeks to support countries to scale up COVID-19 vaccinations as well as routine immunization services.
“The same is true for routine immunization as for COVID-19,” said Helen Rees, executive director of a reproductive health and HIV institute at South Africa’s University of the Witwatersrand.
“There is the direct health… problem, but there’s this spinoff in terms of adversely affecting poor development and contributing to poverty, which is absolutely critical for our region.”
Read more:
Scientists investigate hepatitis outbreak in children in Europe and US
US FDA to publish proposal to ban menthol cigarettes: Report
UN aid chief says two million children risk starving to death in Horn of Africa

 World2 years ago
World2 years ago
 World2 years ago
World2 years ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago
 World7 years ago
World7 years ago
 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years ago